
- Home
- 1. Semester
- Angewandte Physik
- Elektronische Bauelemente
- Ingenieurmathematik 1
- Grundlagen
- Mengen
- Aussagenlogik
- Folgen und Reihen
- Komplexe Zahlen
- Relationen
- Funktionen
- Integralrechnung
- Elektrotechnik 1
- Ladung und Ladungsträger
- Coulombsche Gesetz
- Potential und Spannung
- elektrisches Feld
- elektrischer Fluss
- elektrischer Strom
- elektrische Energie
- elektrische Leistung
- elektrische Widerstand
- spezifischer Widerstand
- magnetisches Feld
- magnetischer Fluss
- magnetische Energie
- magnetische Kraft
- magnetischer Widerstand
- Stromkreis
- Netzwerke
- Kondensator
- Spule
- magnetischer Kreis
- Induktivität
- Grundlagen der Programmierung 1
- 2. Semester
- Digitaltechnik
- Messtechnik
- Signale und Systeme
- Elektrotechnik 2
- Ingenieurmathematik 2
- 3. Semester
- 4. Semester
- Grundlagen der Programmierung 2
- Regelungstechnik
- Mikrocomputertechnik
- Leistungselektronik
- Nachrichtenübertragungs- technik
- Energiespeicher
- 5. Semester
- 6. Semester
- 7. Semester
Elektrotechnik 2
Bei Wechselstrom gilt:
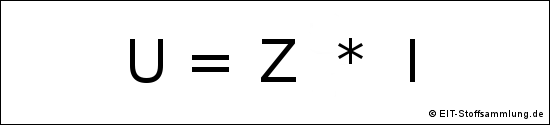
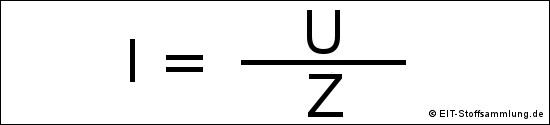
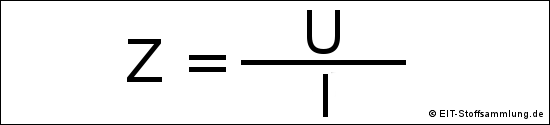
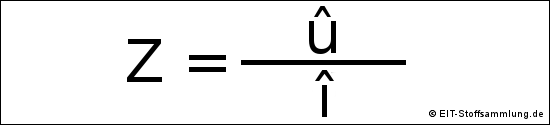


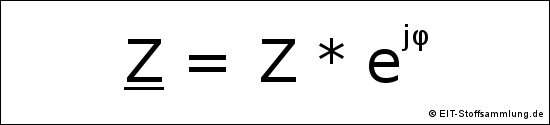
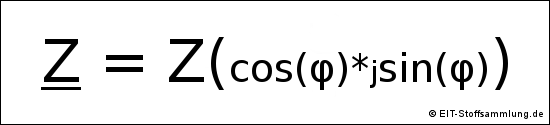
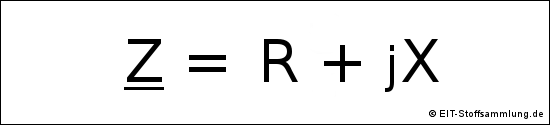
Z = Impedanz oder komplexe Impedanz
Z = |Z| = Scheinwiderstand oder Betrag der Impedanz
Copyright © KN_Scholar 2026
